What Is Bearing Failures Analysis You Need to Know
What Is Bearing Failures Analysis You Need to Know
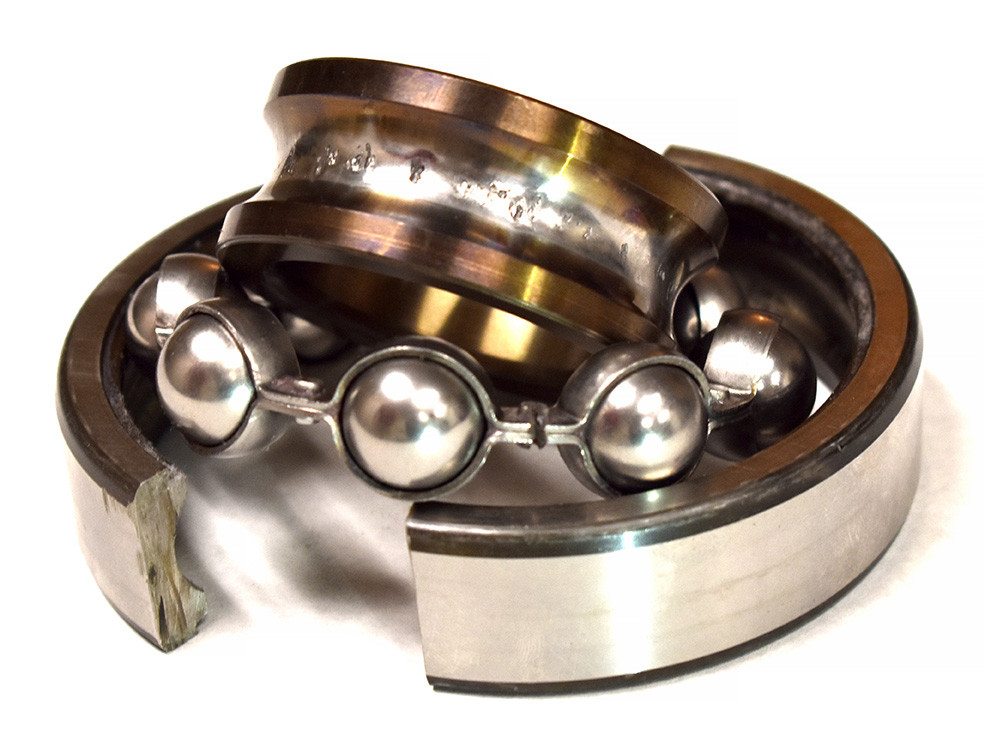
BEARINGS are among the most important machine components in the vast majority of rotating machines because of their carrying capacity and reliability. Generally, a rolling bearing cannot rotate forever. It often works well in non-ideal conditions, but sometimes minor problems cause bearings to fail quickly and mysteriously without any notable warning.
The bearing failures mainly result from excessive wear or damage in rolling ball elements as well as in the inner/outer races of the bearing. Presently real-time condition monitoring systems for bearing systems often fail to provide sufficient time between warnings. And on the other hand, inaccurate interpretation of operational conditions may result in false alarms and associated unnecessary costs and downtime. Traditionally, fault detection has become possible by comparing the sensor signal sensitive features in the machinery while running in normal and faulty conditions.
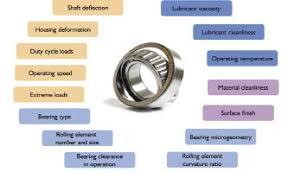
How to detect bearing failures
This method of the detection of faults has shown considerable success and people have developed several techniques. The use of vibration signals is quite common in the field of condition monitoring of rotating machinery. Analyzing the vibration signals directly in the time domain is one of the simplest and cheapest diagnosis approaches. However, as the damage increase, the vibration sign all becomes more random. And the temporary statistical values reduce to more like that of normal bearing levels. This is the most important shortcoming of this approach.
In the frequency domain approach, the major frequency components of vibration signals and use their amplitudes for trending purposes. One of the drawbacks of frequency-domain approaches is that they require the known and pre-estimated factor is bearing defect frequencies.
The time-frequency domain approach uses both time and frequency information allowing for the transient features, such as impacts. However, this approach fails to analyze the continuously smooth signal. In this paper, use the powerful method of QRA to study and characterize the experimental sensor signals. The sensor signal is generated during the normal and faulty states of the bearing under study.