Bearing Seals Type of Deep Groove Ball Bearing
Bearing Seals Type of Deep Groove Ball Bearing
As you know there are many different types of bearings, and a ball bearing (or also known as a “deep groove ball bearing”) is one of them.
Ball bearings are considered to be the most popular because they satisfy a huge variety of operating conditions and performance requirements. The main purpose of this kind of bearing is to reduce rotational friction by supporting radial and axis loads. However, there are also different types of ball bearings with certain constructional features, all catering to your specific needs.
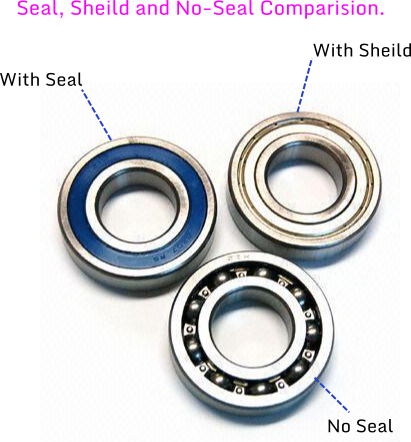

Shielded Ball Bearing
Shielded ball bearings have a metal or plastic shield. This shield is secured to the outer race on each side of the bearing.
This type of bearing adds protection against lubrication migration while also offering protection from contamination of the grease. Grease contamination affects lubrication of the ball bearing, resulting in wear and rust from the metal,which in turn causes additional damage to the bearing.
Now if you want to consider going for a shielded ball type of bearing, you must know that there are also different kinds of shielded ball bearings (which can also be combined with sealed bearings).
§ Z Type
This type of shielded ball bearing has a metal shield on one side while the other side is unshielded. The Z type also has minimal clearance and is the most popular shielded ball bearing type. However, this type of bearing does not work well with heavy load, high speed, or high precision.
§ ZZ Type
Also known as “2 Z”, this type of shielded ball bearing is similar to the Z Type, the only difference is the ZZ type has a separate metal shield on each of its sides. There is also no substantial impact on torque or speed while still being able to function well as an open bearing. It is also worthy to note that once installed, the ZZ type can no longer be removed.
Sealed Ball Bearings
Because of the covers over the balls, sealed ball bearings are similar in structure with the shielded ball bearing, the sealed ball bearing variant offers a higher degree protection from moisture and dirt.
Unfortunately,the protection sealed ball bearings provide comes up with a price. The high contact pressure that is made from the seal being against the rotating inner race greatly increases the friction and torque losses. This also causes a buildup of heat.
Like the shielded ball bearing variant, there are also different types of sealed ball bearings.
§ Type 2RS
The 2RS sealed bearing type has a molded rubber for a seal. The type of rubber used for the type 2RS variant is nitrite, which is then bonded to a steel insert. This type of seal makes contact with the inner ring, which provides better protection in contaminated environments compared to a metal shield. But since the type of seal used is molded rubber, one must take into consideration the type of lubricant that will be used for certain chemicals and lubricants tend to react with rubber.
§ Type 2RU
This type of bearing provides a better protection compared to the ZZ shielded ball bearing type but lacks the increase in torque provided by the 2RS type. It has a molded rubber seal, just like the 2RS, so caution in using certain types of lubricants and chemicals must be observed.
Ball bearings spinning in high speeds need enough lubrication and a clean environment in order to have a long service life, although only a little lubrication is needed, since too much lubrication can increase the rolling resistance, thus generating heat which causes the bearing to fail.
Selecting the right shielded or unshielded bearing for your electric motor plays a vital role as it ensures a long service life. Although we do have to remember that once a ball bearing starts to fail and show signs of wear, the bearing will never improve.
As soon as the bearing shows signs of wear and tear or the bearing starts making noise, it needs to be replaced. Delays in having the bearings replaced may cause the motor to burn out sooner which will further cause other damage to the motor components.