Top 9 Bearing Selection Guide to Improve Bearing Performance
Top 9 Bearing Selection Guide to Improve Bearing Performance
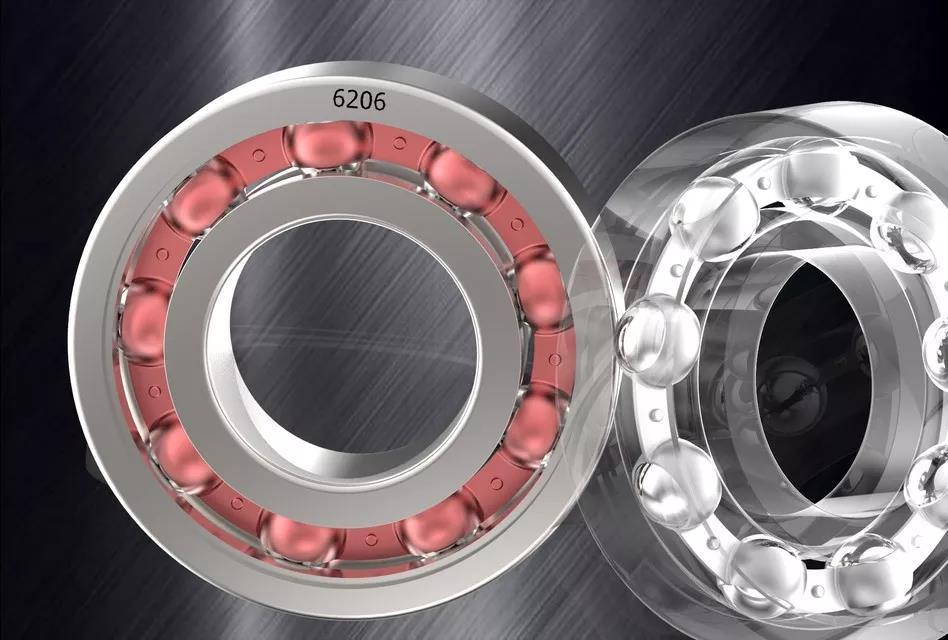

Bearing Selection Guide --- Allow Space
In mechanical design, the size of the shaft is generally determined first, and then select the bearing according to the size of the shaft. Usually, a small shaft chooses the small ball bearing. Select cylindrical roller bearings, spherical roller bearings, tapered roller bearings for the large shaft. But sometimes people use ball bearings. In a restricted radial space of the bearing installation part, use a bearing with a smaller radial section height.
Such as needle roller bearings, certain series of deep groove ball bearings, angular contact ball bearings, cylindrical roller or spherical roller bearings, and thin-walled bearings. If there is a restricted axial space of the bearing installation part, use bearings with smaller width dimensions.
Bearing Load
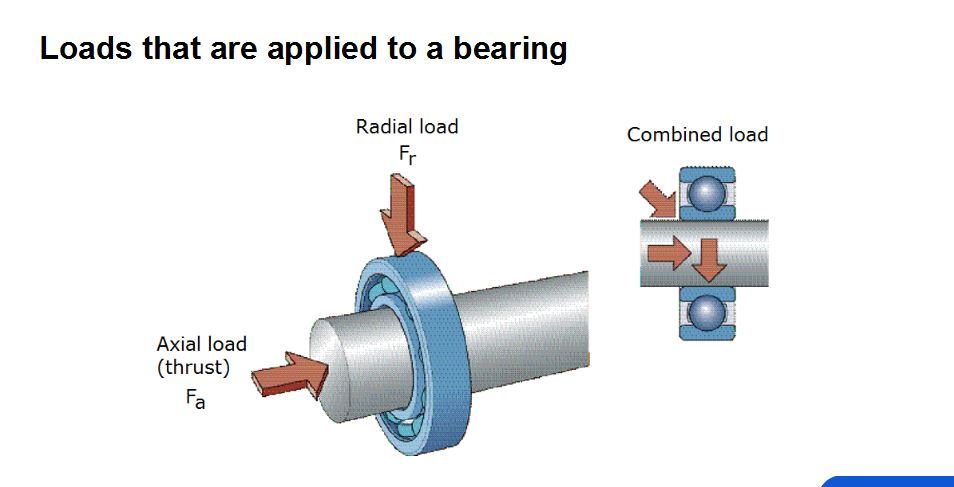
Select deep groove ball bearings and cylindrical roller bearings for a pure radial load. Select thrust ball bearings and thrust cylindrical roller bearings for the pure axial load.
While there is a radial load and axial load (combined load), choose angular contact ball bearings or tapered roller bearings generally. The radial load is large and the axial load is small, you can choose deep groove ball bearings and cylindrical roller bearings with ribs on the inner and outer rings. When there are large shaft or housing deformation and poor installation alignment, select self-aligning ball bearings, and spherical roller bearings. If the axial load is large and the radial load is small, choose thrust angular contact ball bearings. If the four-point contact ball bearing still requires self-aligning performance, you can choose thrust spherical roller bearings.
Bearing Speed
The bearing working speed of the rolling bearing mainly depends on its allowable operating temperature. Bearings with low friction resistance and less internal heating are suitable for high-speed operation.
When only bearing radial load, choose deep groove ball bearings and cylindrical roller bearings to achieve higher speed. Choose angular contact ball bearings if they bear the combined loads.
Specially designed high-precision angular contact ball bearings can reach extremely high speeds. The speed of various thrust bearings is lower than that of radial bearings.
Bearing Rotation Accuracy
Bearing Selection Guide --- Rigidity
Amount of elastic deformation that occurs when the bearing is loaded determines the rigidity of the rolling bearing. Under normal circumstances, this kind of deformation is very small and can be ignored. But in some machinery, such as a machine tool spindle system, the static stiffness and dynamic stiffness of the bearing have a great influence on the characteristics of the system.
Generally speaking, roller bearings have higher stiffness than ball bearings. Various types of bearings can also improve rigidity to varying degrees through proper "preloading".
Noise and Vibration
Axial Movement
The most common way to configure bearings is to install a set of axially positioned "same bearings" on one end of the shaft. And install a set of axially movable "floating bearing" on the other end. To prevent the shaft from being stuck due to thermal expansion and contraction. The frequently used "floating bearing" is a cylindrical roller bearing with no ribs on the inner or outer ring. Sometimes use non-separable deep groove ball bearings or spherical roller bearings as floating bearings.
However, when installing the inner ring and the shaft or outer ring and the housing hole, you should select the clearance fit to ensure that the inner ring or the outer ring has sufficient axial movement freedom.
Friction Torque
The friction resistance of ball bearings is lower than that of roller bearings. When a pure radial load is applied, the friction resistance of radial contact bearing is small. Apply a pure axial load, the friction resistance of axial contact bearing is small. In a combined load, the friction resistance of the angular contact bearing whose bearing contact angle is close to the load angle is the smallest.
Low friction torque bearings should avoid the use of contact seals. At the same time, it is better to use drip lubrication, oil-air lubrication, or other lubrication methods that are conducive to reducing wear.
Bearing Installation and Removal
Use bearings with cylindrical bores are in machines that are frequently installed and disassembled. It's better to use Separable angular contact ball bearings, tapered roller bearings, separable cylindrical roller bearings, needle roller bearings, and thrust bearings.
Install the bearing with a conical inner hole on the journal, or on the cylindrical journal with the aid of an adapter sleeve or a withdrawal sleeve, which is very convenient for installation and disassembly.