7 Effective Bearing Damage Analysis on Why You Replace Bearings Frequently
7 Effective Bearing Damage Analysis on Why You Replace Bearings Frequently
Bearing damage analysis is a very important step to maintain your machines. Due to the quality and external conditions of the rolling bearing during use, its bearing capacity, rotation accuracy, and anti-friction performance will change. When the performance index of the bearing is lower than the use requirement and cannot work normally, it is bearing damage or failure.
Once the bearing has damage or other accidents, its machinery and equipment will stop rotating and damage its functions. It only manifests itself until it accumulates to a certain level, that is, it does not deteriorate until it reaches a certain level. Of course, the damage of rolling bearings is much more complicated than the damage of general mechanical parts.
The characteristics of rolling bearing damage analysis are many manifestations and complex reasons. In addition to the internal factors of bearing design and manufacturing, most of the damage to the bearing is due to improper use.
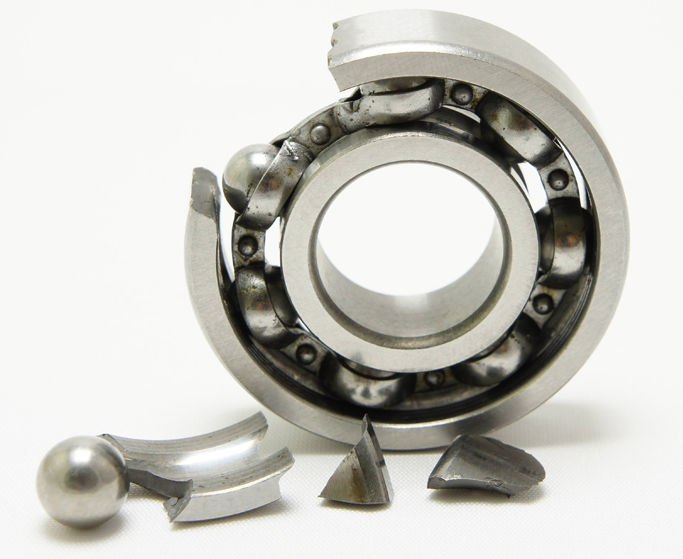

Metal corrosion occurs

Oxidative wear
The tiny peaks and valleys on the friction surface extrude each other, causing the brittle surface layer to gradually fall off and wear. The tiny peaks and valleys on the surface of the relative motion of the bearing are in touch with oxidation in the air to form brittle oxide. The oxide is very easy to fall off during friction, and the wear that occurs is oxidative wear.
Friction generates heat wear
When the bearing is working under high speed, heavy load, and poor lubrication, the peaks and valleys of the surface will generate high temperatures due to friction. The hardness and wear resistance of the contact points decrease, and even adhesion and tearing occur.
Hard wear
If the bearing moves relative to each other, the surface organization of the bearing movement is uneven and there are hard particles. Impurities such as sand, friction, and cutting chips fall between the moving surface of the bearing. During the relative movement of the bearing, hard particles or impurities will scratch the bearing surface and even form grooves.
Pitting wear
Gears, bearings, etc. are in rolling contact with the surface, and are periodically subjected to large contact pressure during the relative process. Long-term action, fatigue phenomenon occurs on the surface of the metal, causing micro-cracks and erosion on the surface of the bearing.
Bearing overload or improper use
Bearing clearance is too small
The front wheel of the car is a diagonal thrust bearing, which needs to adjust the gap. Too loose will cause abnormal noise, deflection, and wheel shaking. Too tight will accelerate wear, both are bad. For old bearings, check for burrs, scratches, and cracks on the surface of the ball (column).
Whether the radial clearance and axial clearance of the old bearing are up to standard, generally you only measure the radial clearance. For new bearings, first, check whether the bearing model is correct. For example, Model 6318 deep groove ball bearing, bearing inner diameter 90mm, its radial clearance range is 0.016~0.046mm.
Use inferior bearings
Poor installation
To install the bearing, follow the installation steps of the bearing, do not install and dismantle brutally. Whether you install the bearing correctly or not is related to the service life of the bearing, so everyone must pay attention to it. Avoid holding the bearing directly with your hands when installing the bearing, because sweat on your hands may also cause corrosion.
When installing the bearing, the most important thing is not to allow strong punching or to directly hit the bearing with a hammer. There is also no pressure to pass through the rolling elements.