Complete Information on Bearing Preload for 2021 [Easy]
Take the deep groove ball bearing as an example.
If there is no pretension, there is a play between the top of the bearing and the shaft. When the shaft receives a downward force, the ball at the bottom of the bearing is compressed and elastically deformed. And that causes the theoretical axis of the shaft to move down a larger distance.
And if there is pretension, it is as shown in Figure b, because the rolling element has been subjected to pressure (pressure applied in the axial direction), and has produced a certain elastic deformation. When the same radial pressure as in Figure a is applied, the bottom ball Elastic deformation will also occur, but the amount of deformation is not as large as shown in Figure a.
That is to say, when there is pretension, the distance that the theoretical axis of the shaft moves downward is reduced.
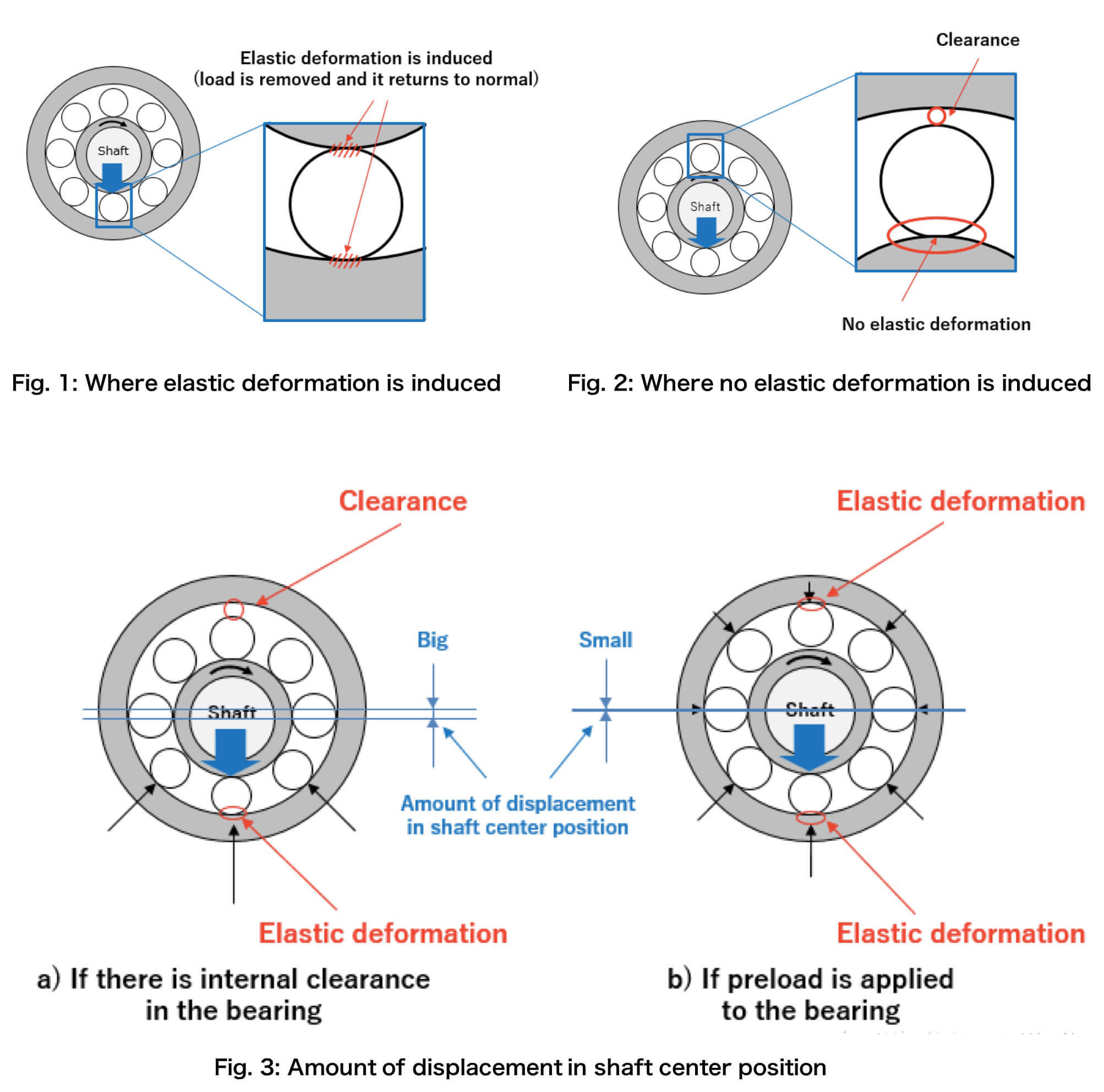
This is the difference between preload and no preload
Preload improves rigidity, and of course, it also improves transmission accuracy.
The core of preloading is to apply an external force in advance. So that the rolling elements and the inner and outer rings of the bearing are in close contact. And that is resulting in a certain amount of elastic deformation.
In fact, the nut at the left end exerts a rightward force. Part of this force acts on the sphere through the inner ring of the left bearing. And then is transmitted to the outer ring and outer positioning sleeve. And part of the force is transmitted to the inner positioning sleeve through the inner ring of the bearing.
Of course, because the rotation of the left end nut will drive the shaft to move to the left. The shoulder on the right side of the shaft will exert a force on the inner ring of the right bearing. And this force will eventually be transmitted to the inner and outer positioning sleeves. And from the left the force is balanced.
When the force applied by the inner positioning sleeve material and the left end nut is constant. The size of the pre-pressure F1 depends on the size of the inner positioning sleeve. Because it determines the position that the inner ring of the bearing can reach.
A more appropriate situation
It can be imagined that a more appropriate situation. That the size of the inner positioning sleeve is the same as that of the outer positioning sleeve. And the pre-tightening force F1 is applied by a certain deformation of the inner positioning sleeve.
If the size of the inner positioning sleeve becomes longer. The worse situation is that the force on the nut cannot be applied to the sphere. And it is all absorbed by the inner positioning sleeve, and the pre-tightening force cannot be generated.
If the size of the inner positioning sleeve becomes shorter. The worst case is that the force on the nut will not be transmitted to the inner positioning sleeve at all. And all will be absorbed by the outer positioning sleeve. At this time, it is equivalent to no inner positioning sleeve.
OK, here, we understand what preload is and what is positioning preload.

So what is constant pressure preloading?
Very simple, it is to rely on structures such as coil springs or wave shrapnel to apply constant pressure.
Because the spring and the shrapnel are not sensitive to small displacements. Its pre-tightening force fluctuates very little and remains basically unchanged, so it is called constant pressure pre-compression.
At this point, we found that the pre-tension of the bearing and the pre-tension of the ball screw (even the pre-tension of the guide rail, such as the pre-tension of the cross-roller guide) are essentially the same. And they are both to make the rolling body and the attachment body close. Contact, produce certain elastic deformation to improve rigidity and precision.
In engineering, we use 3 types of bearings, angular contact ball bearings and tapered roller bearings, and deep groove ball bearings.
Angular contact ball bearings and tapered roller bearings must be preloaded.
The deep groove ball bearing can be preloaded or not. But it is best to have the pretension to prevent vibration and noise. We generally use wave springs to pretension, because it takes up less space.
Regarding the preload structure of the bearing, the purpose of the preload and the characteristics of the preload, the amount of preload, etc., here are two tables. I think it is a good summary. Paste it and leave a record for future reference.
As mentioned above, the preload is set in advance.